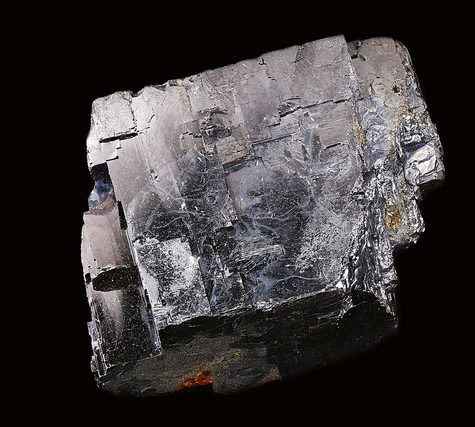
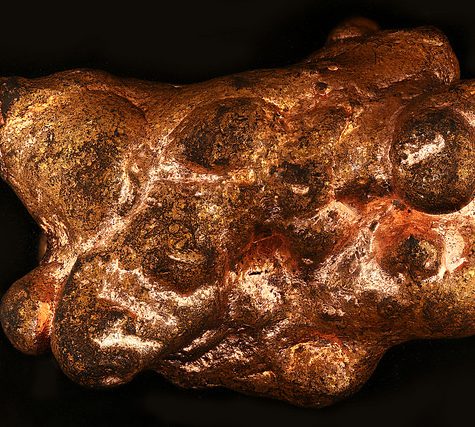
Galena is the main ore of lead, used since ancient times. Because of its somewhat low melting point, it was easy to liberate by smelting. It typically forms in low-temperature sedimentary deposits.
In some deposits galena contains about 1–2% silver, a byproduct that far outweighs the main lead ore in revenue. Galena deposits often also contain significant amounts of silver as included silver sulfide mineral phases or as limited solid solution within the galena structure. These argentiferous galenas have long been the most important ore of silver.[citation needed]
Galena deposits are found worldwide in various environments. Noted deposits include those at Freiberg in Saxony; Cornwall, the Mendips in Somerset, Derbyshire, and Cumberland in England; the Madan, Rhodope Mountains in Bulgaria; the Sullivan Mine of British Columbia; Broken Hill and Mount Isa in Australia; and the ancient mines of Sardinia. Galena also occurs in North African countries and at Mount Hermon in Northern Israel. In the United States, it occurs most notably in the Mississippi Valley type deposits of the Lead Belt in southeastern Missouri, and in the Driftless Area of Illinois, Iowa and Wisconsin. The economic importance of galena to the early history of the Driftless Area was so great that one of the towns in the region was named Galena, Illinois.
Galena also was a major mineral of the zinc-lead mines of the tri-state district around Joplin in southwestern Missouri and the adjoining areas of Kansas and Oklahoma. Galena is also an important ore mineral in the silver mining regions of Colorado, Idaho, Utah and Montana. Of the latter, the Coeur d’Alene district of northern Idaho was most prominent.
Galena is the official state mineral of the U.S. states of Missouri and Wisconsin; the former mining communities of Galena, Kansas and Galena, Illinois take their names from deposits of this mineral.
Derbyshire in the UK was one of the main areas where galena was mined.
The largest documented crystal of galena is composite cubo-octahedra from the Great Laxey Mine, Isle of Man, measuring 25 cm × 25 cm × 25 cm (10 in × 10 in × 10 in).