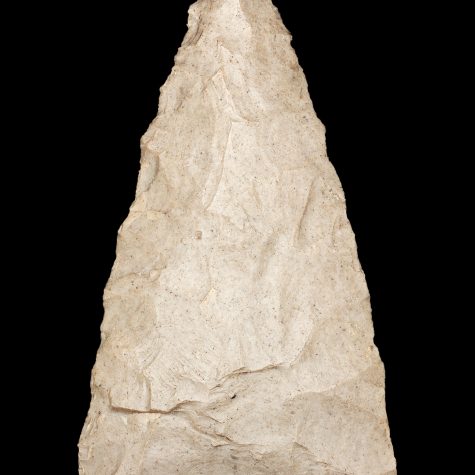
The bow and arrow represents one of the great technological advancements in weaponry in the ancient world. In fact, the bow is the first mechanical device that could store energy, as the arrow was held in the string before its release. Recent distance records in flight archery for pulled bows are around one third mile, the longest crossbow shot is 1.16 miles! Bows and arrows were used just about everywhere in the world except Australia where spear throwers were the preferred weapon. Triangular shaped arrow points were one of the most common types of arrow points used on the tips of arrows.

The Willow Tree series was replaced because of a new technology. Rather than simply using the older hammer striking method Richard Doty has suggested Hull changed to a rocker arm press. The dies needed for a rocker arm press were quite different from dies used in the hammer strike method. A rocker press used large-sized rectangular shaped dies with a curved face so that the die could rock back and forth. The image for the coin was then engraved on the curved face of the rocker, one rocker for the obverse and another for the reverse (click here for picture of rocker dies). The two rocker dies would then be mounted face to face in the press. By pulling a lever the upper and lower rockers would press against each other with a rolling motion (click here for picture of a rocker press). As long as the two dies were properly aligned a blank planchet placed between them would be impressed with the design of the dies.
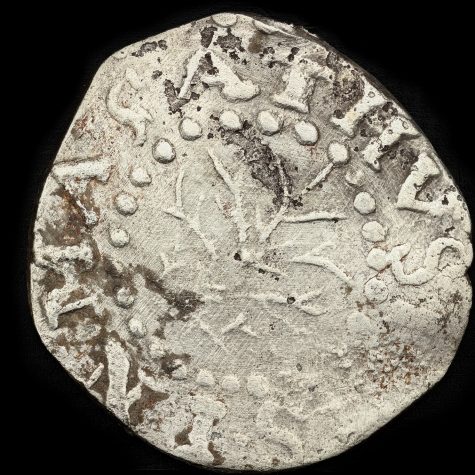

The Willow Tree series was replaced because of a new technology. Rather than simply using the older hammer striking method Richard Doty has suggested Hull changed to a rocker arm press. The dies needed for a rocker arm press were quite different from dies used in the hammer strike method. A rocker press used large-sized rectangular shaped dies with a curved face so that the die could rock back and forth. The image for the coin was then engraved on the curved face of the rocker, one rocker for the obverse and another for the reverse (click here for picture of rocker dies). The two rocker dies would then be mounted face to face in the press. By pulling a lever the upper and lower rockers would press against each other with a rolling motion (click here for picture of a rocker press). As long as the two dies were properly aligned a blank planchet placed between them would be impressed with the design of the dies.

Need an extra shutter cable?
If a hardware component of the Macropod product line is in need of repair and out of warranty, please purchase a repair request and send your part to:
The total cost covers component repair, testing, cleaning and return postage.
Thank you for choosing Macroscopic Solutions!
|
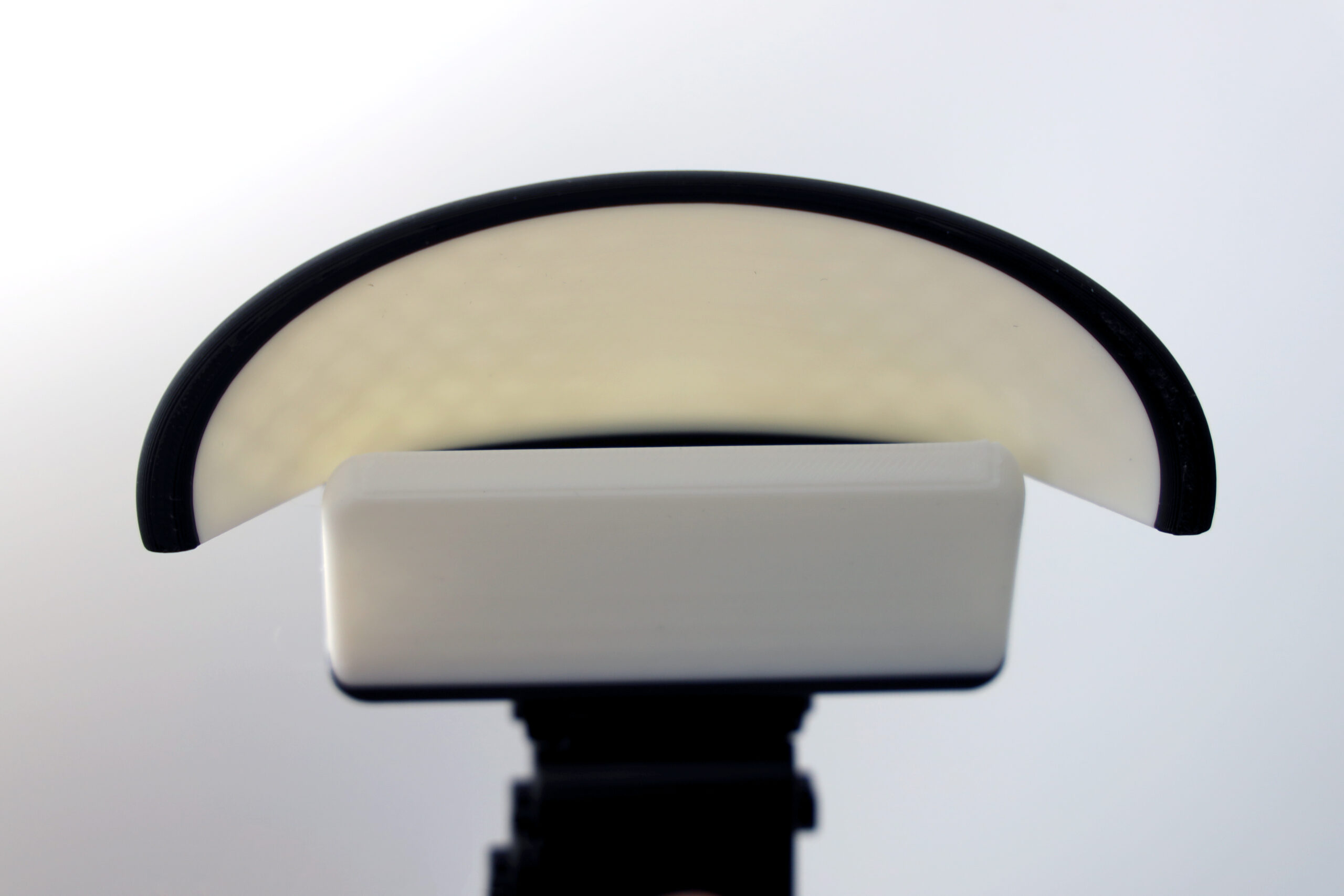
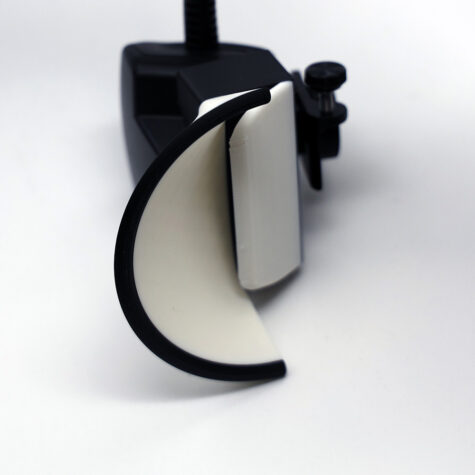
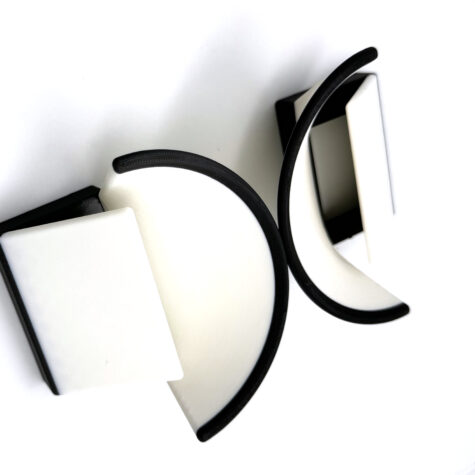
This diffuser is custom designed for the Godox MF12 Twin Lite Macro Flash. The inner deflector reflects light onto the conical structure of the diffuser. This section projects soft light onto your subject without losing too much light form the source. These diffusers are a must have for any photographer working with the MF12 Flash by Godox! These dual diffusers no longer warm the subject and cast a brighter, more lively look onto your subject. Phew!! A rigid macro diffuser that withstands heavy field use. Mirror tests shown below indicate the level of diffusion offered by the Turtledove Diffusers. Flash and camera settings are at Flash 1/32, EXP 1/200, f4.0, and ISO 200. |
This diffuser is custom designed for the Canon MT-26EX-RT Twin Lite Macro Flash. The inner deflector reflects light onto the conical structure of the diffuser. This section projects soft light onto your subject without losing too much light form the source. These diffusers are a must have for any photographer working with the MT-26EX-RT Flash by Canon!
These dual diffusers no longer warm the subject and cast a brighter, more lively look onto your subject. Phew!! A rigid macro diffuser that works well in heavy field use.
Mirror tests shown below indicate the level of diffusion offered by the Turtledove Diffusers. Flash and camera settings are at Flash 1/32, EXP 1/200, f4.0, and ISO 200.
This diffuser is custom designed for the Yongnuo YN-24EX TTL Twin Lite Macro Flash. The inner deflector reflects light onto the conical structure of the diffuser. This section projects soft light onto your subject without losing too much light form the source. These diffusers are a must have for any photographer working with the YN-24EX TTL Flash by Yongnuo!
These dual diffusers no longer warm the subject and cast a brighter, more lively look onto your subject. Phew!! A rigid macro diffuser to withstand heavy field use.
Mirror tests shown below indicate the level of diffusion offered by the Turtledove Diffusers. Flash and camera settings are at Flash 1/32, EXP 1/200, f4.0, and ISO 200.
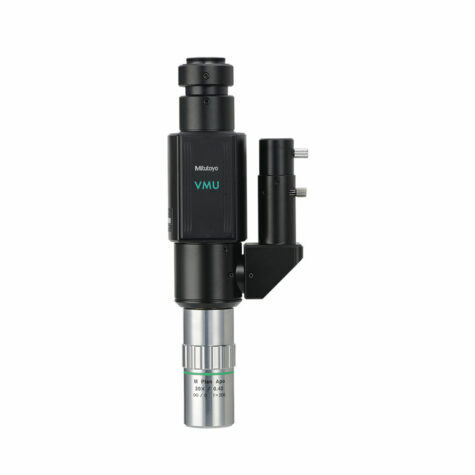
Adapter designed to adapt the Mitutoyo LWD objectives to a lens with 77mm adapter.
This diffuser is custom designed for the Canon MT-24EX Twin Lite Macro Flash. The inner deflector reflects light onto the conical structure of the diffuser. This section projects soft light onto your subject without losing too much light form the source. These diffusers are a must have for any photographer working with the MT-24 EX Flash by Canon!
NOTE* This older diffuser shown in the video below created a slight warming effect and a manual color temperature of ~5000 K needed to be used to mitigate. These dual diffusers no longer warm the subject and cast a brighter, more lively look onto your subject. Phew!! A rigid macro diffuser to withstand all heavy field use.
Mirror tests shown below indicate the level of diffusion offered by the Turtledove Diffusers. Flash and camera settings are at Flash 1/32, EXP 1/200, f4.0, and ISO 200.
$49
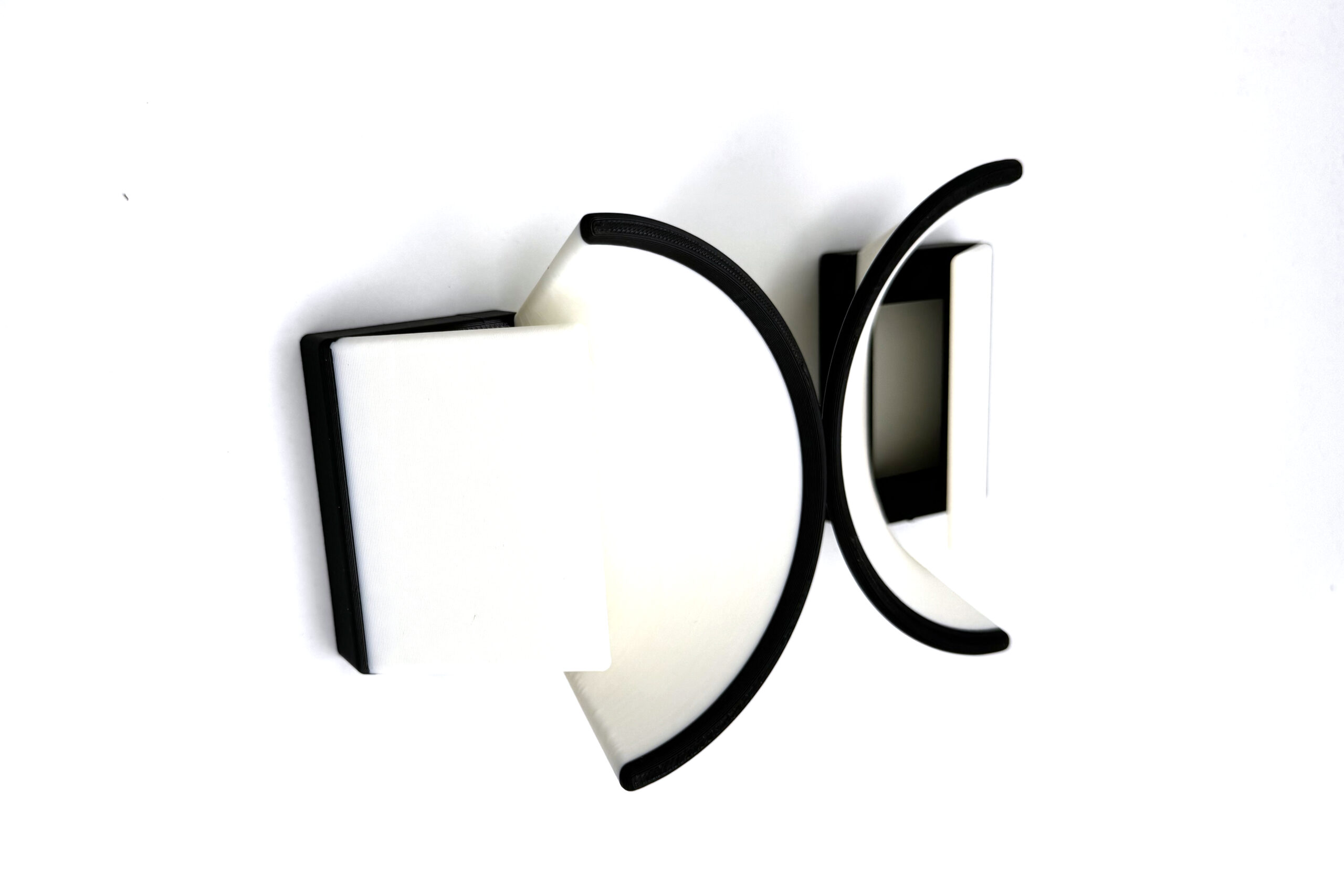
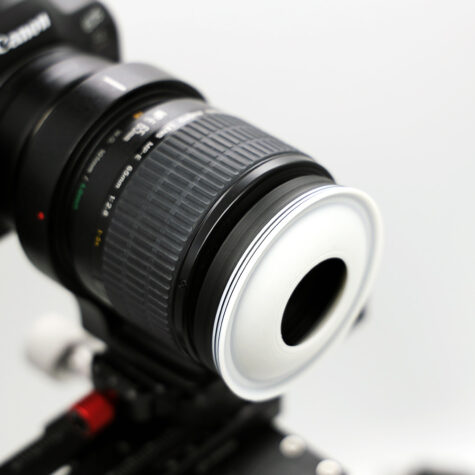
This diffuser is custom designed for the Canon RF 100mm lens and incorporates a snug one-directional twist lock fit. The length of this diffuser provides enough flexibility to get the most out of your working distances while maximizing the amount of light that gets reflected back onto your target. Made to work under close working distances only. The front nose cup design reflects light around the sides of the specimen in combination with an integrated Lieberkuhn reflector to maximize retro-reflectance and illumination. This diffuser is a must have for any photographer working with the RF 100 mm Macro lens by Canon!
Customer Feedback
“I’m finding the model I have is improving my light a lot.” – Nolie
$49
This diffuser is custom designed for the Canon MP-E 65mm 1-5x lens. The length of this diffuser provides enough flexibility to get the most out of your working distances along the 1-5x range, while maximizing the amount of light that gets reflected back onto your target. The dome design reflects light around the sides of the specimen in combination with an integrated Lieberkuhn reflector to maximize retro-reflectance and illumination. This diffuser is a must have for any photographer working with the MP-E 65 mm 1-5x lens by Canon!
Customer Feedback
“I’m finding the model I have is improving my light a lot.” – Nolie
$49.00
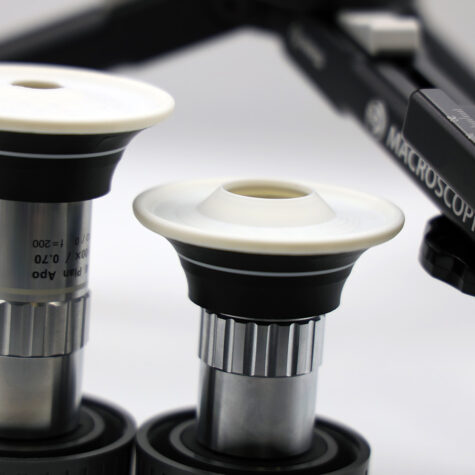
On a microscope or on a photographic system, like the Macropod PRO 3D, this diffuser set (3 in total) yield phenomenal results. They are custom designed for the Mitutoyo M Plan APO Objectives and can combine the properties of reflected and transmitted illumination. Using focus staking techniques, the lens shades stop light from entering the objectives glass while the white surface reflects diffuse light onto the sample. When observing microscope slides, the diffusers can reflect transmitted light back onto opaque materials such as gold and iron inclusions found in geological thin sections.
The diffuser with the smallest aperture with shade is for the 50-100x range, the diffuser with a large aperture with shade is for the 7.5-20x range and the diffuser with a large aperture and no shade is for the 1x-5x range. The shade is a Lieberkuhn reflector designed to stop light from entering the objective at the source. The white reflective surface is designed to softly illuminate the sample. These diffusers work exceptionally well for the Mitutoyo range.
Customer Feedback
“I’m finding the model I have is improving my light a lot.” – Nolie
The Nyholm lab studies beneficial host-microbe interactions between the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, and the bioluminescent bacterium, Vibrio fischeri. Hawaiian bobtail squid are nocturnal predators, remaining buried under the sand during the day and coming out to hunt for shrimp at night neat coral reefs. The squid have a light organ on their underside that houses a colony of glowing bacteria (V. fischeri). The squid uses this bacterial bioluminescence in a form of camouflage called counter-illumination, masking it’s silhouette by matching moonlight and starlight; thus hiding from predators swimming below. The light organ is attached to the ink sac and it can use this ink like a type of shutter to control the amount of light. This likely helps the squid adjust to variable light conditions, for example cloudy nights or a full vs. new moon. In this image of a juvenile squid, you can clearly see the bi-lobed light organ and ink sac in the center of the squid’s mantle cavity.
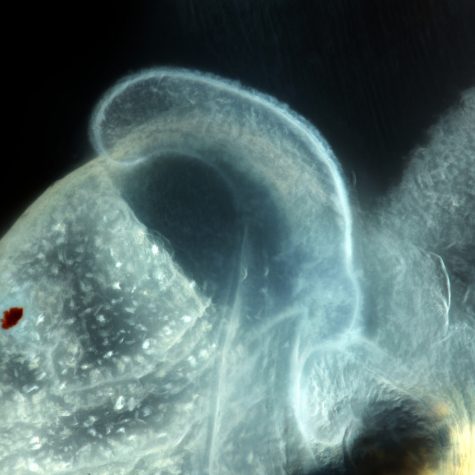
The Hawaiian bobtail squid lay their eggs in clutches on the sea floor, where they take approximately three weeks to develop. This series of macropod images allows us to see the developing squid and monitor embryogenesis. Once the squid hatch, V. fischeri from seawater colonize the light organ within hours. This macropod image allows us to see a close-up view of the ciliated appendage-like structure found on the surface of the juvenile squid’s light organ. Once the squid hatches, the cilia assist in bringing V. fischeri in the seawater to pores at the base of the light organ. These pores lead to inner crypts, where only V. fischeri can enter and colonize. V. fischeri is a relatively rare member of the seawater bacterial community, making up less than 0.1%. The Nyholm lab is trying to understand how the squid’s immune system can differentiate between the symbiont and all the other different kinds of bacteria in seawater.
While the light organ of the squid exemplifies a highly specific beneficial relationship between bacteria and host to provide camouflage at night, this organ is only found in some squid species. All squid, however, are capable of another type of camouflage, cryptic coloration. Squid skin contains special pigmented cells called chromatophores that can change the overall color of the squid in seconds. Each chromatophore contains pigment granules surrounded by nerve and muscle fibers. When these muscles are contracted, the pigment sac expands, creating a larger surface area of color. When the muscles relax, the pigment sac can shrink to a small dot, 15 times smaller than their expanded size, hiding the color. In these macropod images you can see relaxed chromatophores on the mantle and contracted chromatophores around the eyes. The macropod images allow us to see these pigment cells in great detail.




















