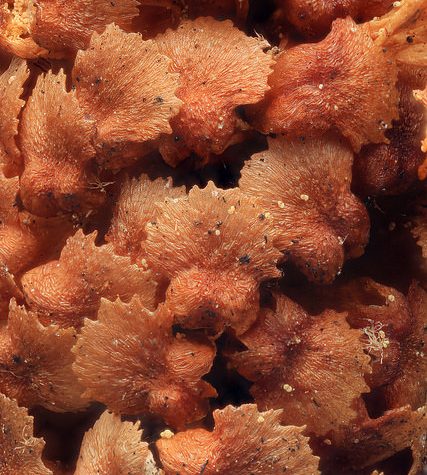
A pine is any conifer in the genus Pinus, /ˈpiːnuːs/,[1] of the family Pinaceae. Pinus is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The Plant List compiled by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts 126 species names of pines as current, together with 35 unresolved species and many more synonyms.[2]
Category of subjects not yet properly identified.

A pine is any conifer in the genus Pinus, /ˈpiːnuːs/,[1] of the family Pinaceae. Pinus is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The Plant List compiled by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts 126 species names of pines as current, together with 35 unresolved species and many more synonyms.[2]
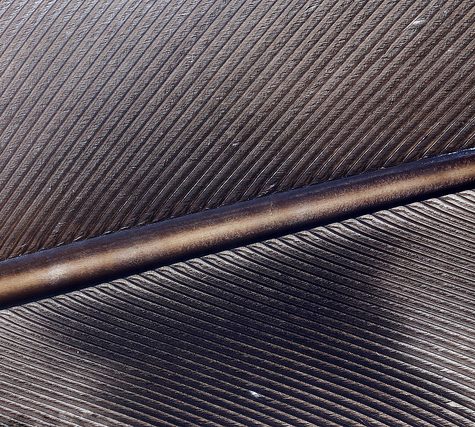

Feathers are epidermal growths that form the distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on birds. They are considered the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates[1][2] and a premier example of a complex evolutionary novelty.[3]They are among the characteristics that distinguish the extant birds from other living groups.[4]
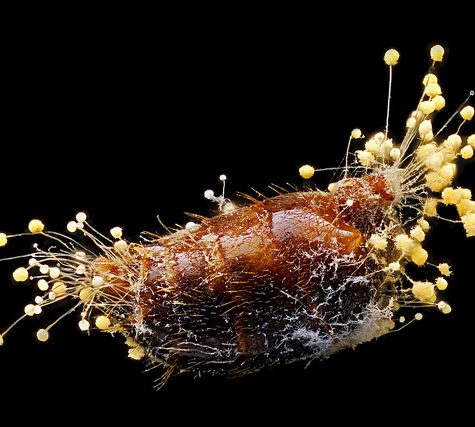

A fungus (plural: fungi[3] or funguses[4]) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from the other eukaryotic life kingdoms of plants and animals.
A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Similar to animals, fungi are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesise. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), which share a common ancestor (form a monophyletic group), an interpretation that is also strongly supported by molecular phylogenetics. This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology (from the Greek μύκης mykes, meaning “fungus”). In the past, mycology was regarded as a branch of botany, although it is now known fungi are genetically more closely related to animals than to plants.
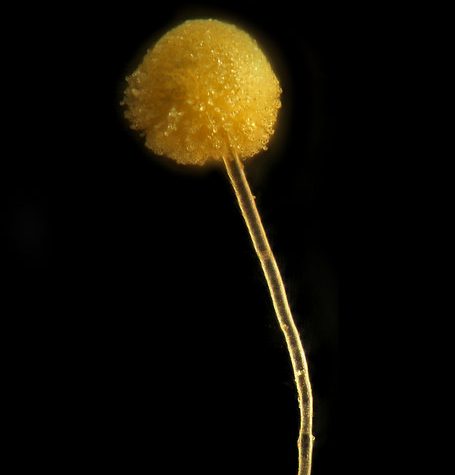
A fungus (plural: fungi[3] or funguses[4]) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from the other eukaryotic life kingdoms of plants and animals.
A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Similar to animals, fungi are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesise. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), which share a common ancestor (form a monophyletic group), an interpretation that is also strongly supported by molecular phylogenetics. This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology (from the Greek μύκης mykes, meaning “fungus”). In the past, mycology was regarded as a branch of botany, although it is now known fungi are genetically more closely related to animals than to plants.

For the purpose of reproduction most amphibians require fresh wateralthough some lay their eggs on land and have developed various means of keeping them moist. A few (e.g. Fejervarya raja) can inhabit brackish water, but there are no true marine amphibians.[66] There are reports, however, of particular amphibian populations unexpectedly invading marine waters. Such was the case with the Black Sea invasion of the natural hybrid Pelophylax esculentus reported in 2010.[67]

For the purpose of reproduction most amphibians require fresh wateralthough some lay their eggs on land and have developed various means of keeping them moist. A few (e.g. Fejervarya raja) can inhabit brackish water, but there are no true marine amphibians.[66] There are reports, however, of particular amphibian populations unexpectedly invading marine waters. Such was the case with the Black Sea invasion of the natural hybrid Pelophylax esculentus reported in 2010.[67]

Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by a lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All present-day salamander families are grouped together under the scientific name Urodela. Salamander diversity is most abundant in the Northern Hemisphere and most species are found in the Holarctic ecozone, with some species present in the Neotropicalzone.

Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by a lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All present-day salamander families are grouped together under the scientific name Urodela. Salamander diversity is most abundant in the Northern Hemisphere and most species are found in the Holarctic ecozone, with some species present in the Neotropicalzone.

Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by a lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All present-day salamander families are grouped together under the scientific name Urodela. Salamander diversity is most abundant in the Northern Hemisphere and most species are found in the Holarctic ecozone, with some species present in the Neotropicalzone.

Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by a lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All present-day salamander families are grouped together under the scientific name Urodela. Salamander diversity is most abundant in the Northern Hemisphere and most species are found in the Holarctic ecozone, with some species present in the Neotropicalzone.

Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by a lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All present-day salamander families are grouped together under the scientific name Urodela. Salamander diversity is most abundant in the Northern Hemisphere and most species are found in the Holarctic ecozone, with some species present in the Neotropicalzone.

Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by a lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All present-day salamander families are grouped together under the scientific name Urodela. Salamander diversity is most abundant in the Northern Hemisphere and most species are found in the Holarctic ecozone, with some species present in the Neotropicalzone.
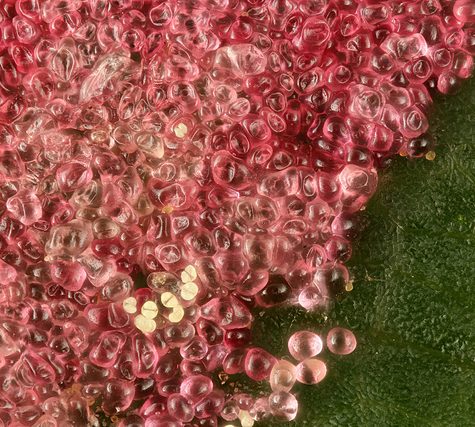

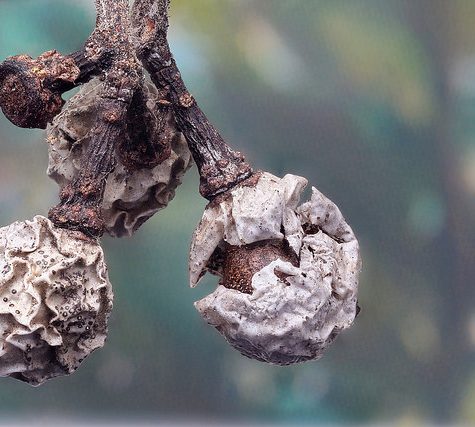
Galls or cecidia are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths[1] of plant tissues, similar to benign tumors or warts in animals. They can be caused by various parasites, from fungi and bacteria, to insects and mites. Plant galls are often highly organized structures and because of this the cause of the gall can often be determined without the actual agent being identified. This applies particularly to some insect and mite plant galls. The study of plant galls is known as cecidology.
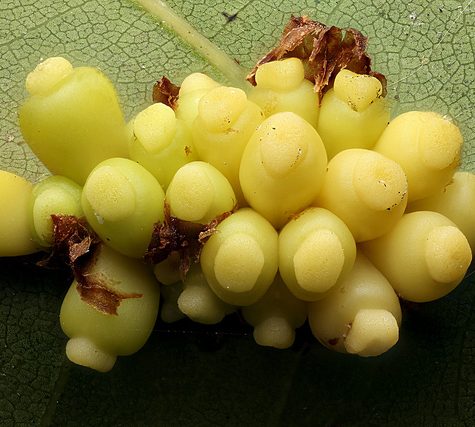

Galls or cecidia are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths[1] of plant tissues, similar to benign tumors or warts in animals. They can be caused by various parasites, from fungi and bacteria, to insects and mites. Plant galls are often highly organized structures and because of this the cause of the gall can often be determined without the actual agent being identified. This applies particularly to some insect and mite plant galls. The study of plant galls is known as cecidology.

