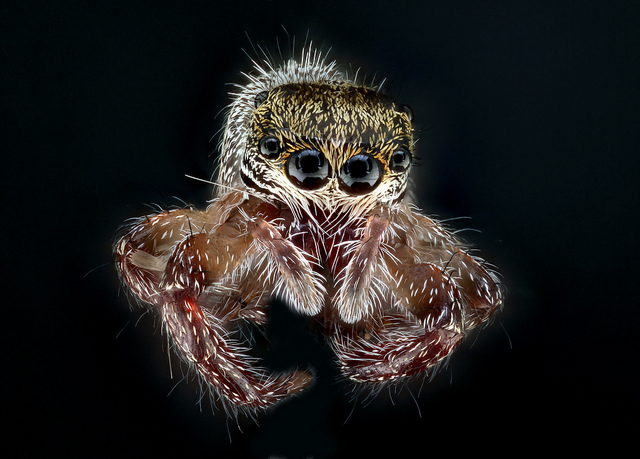
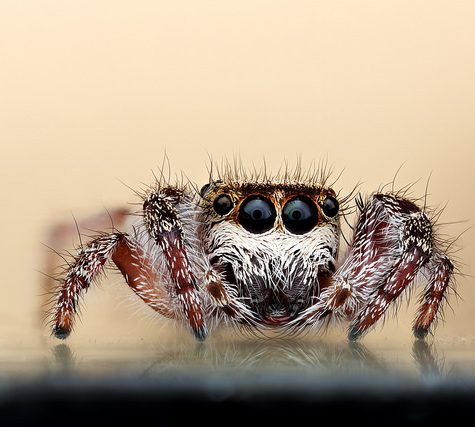
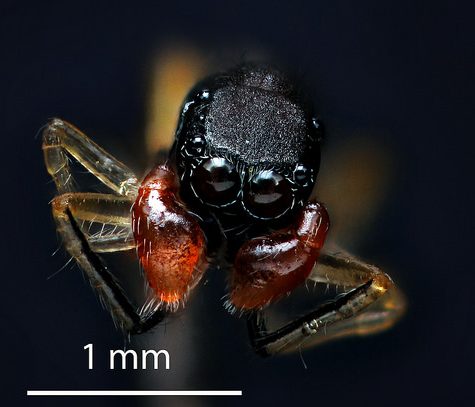
Phidippus princeps is a rare species of jumping spider found in Canada and the United States. These jumping spiders’ vision exceeds by a factor of ten that of dragonflies, which have the best vision among insects.
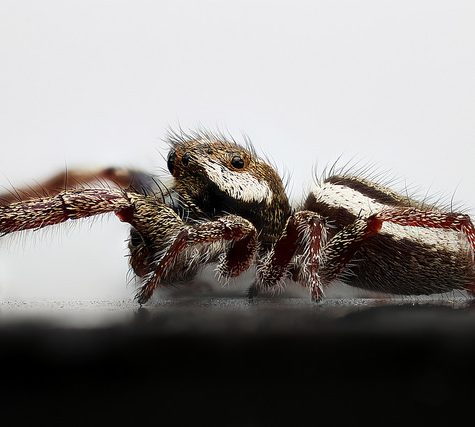

Phidippus princeps is a rare species of jumping spider found in Canada and the United States. These jumping spiders’ vision exceeds by a factor of ten that of dragonflies, which have the best vision among insects.

Dermacentor variabilis, also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia (Francisella tularensis). It is one of the most well-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host, which could take several days for the host to experience some symptoms.
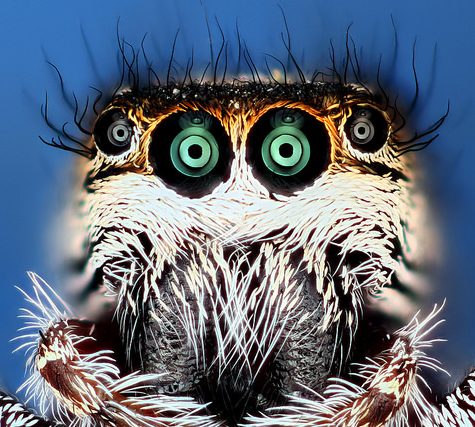

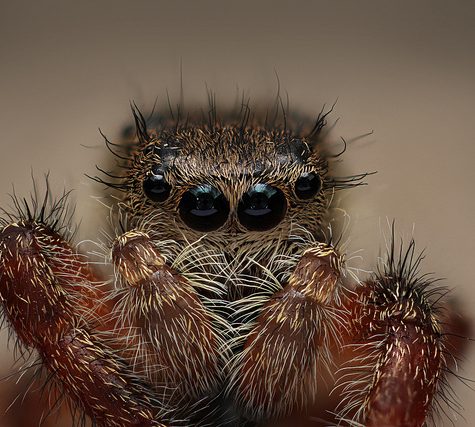
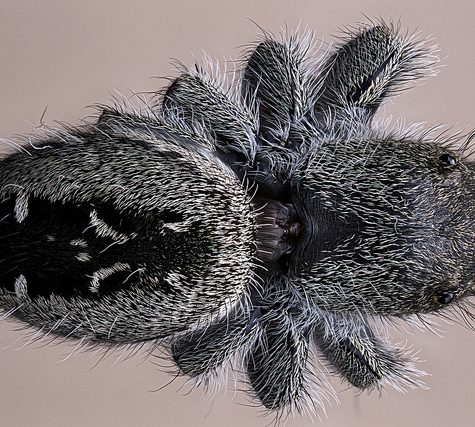
The jumping spider family (Salticidae) contains over 600 described genera and more than 5800 described species,[1] making it the largest family of spiders with about 13% of all species.[2] Jumping spiders have some of the best vision among arthropods and use it in courtship, hunting, and navigation. Although they normally move unobtrusively and fairly slowly, most species are capable of very agile jumps, notably when hunting, but sometimes in response to sudden threats or crossing long gaps. Both their book lungsand tracheal system are well-developed, and they use both systems (bimodal breathing). Jumping spiders are generally recognized by their eye pattern. All jumping spiders have four pairs of eyes, with the anterior median pair being particularly large.
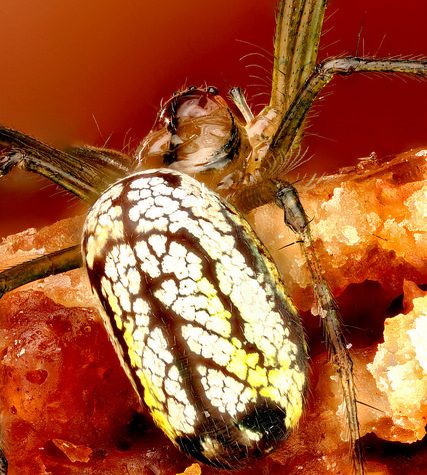

Leucauge venusta, known as the orchard spider, is a long-jawed orbweaver spider that occurs from southern Canada to Colombia, along the East coast, reaching into the central US. The web is often oriented horizontally, with the spider hanging down in the center.
It is distinctively colored, with leaf-green legs and sides (which can sometimes vary to a dark green or even orange). The underside of its thorax is spotted with yellow and black, the top is silvery with brown and black streaks. The neon yellow, orange or red spots on the rear of the abdomen are variable in size among individuals and sometimes absent.
This species is parasitised by a wasp larva which attaches itself externally at the junction of the cephalothorax and abdomen.[1]
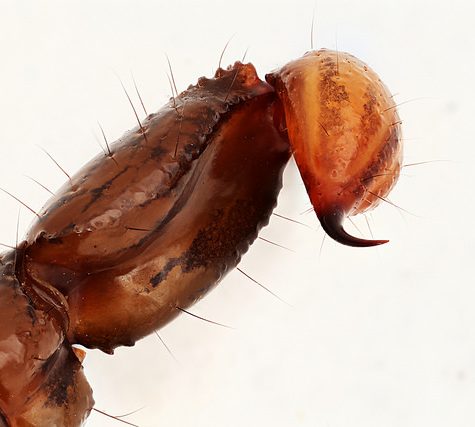

Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs[1] and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping pedipalps and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger. Scorpions range in size from 9 mm / 0.3 in. (Typhlochactas mitchelli) to 23 cm / 9 in. (Heterometrus swammerdami).[2]
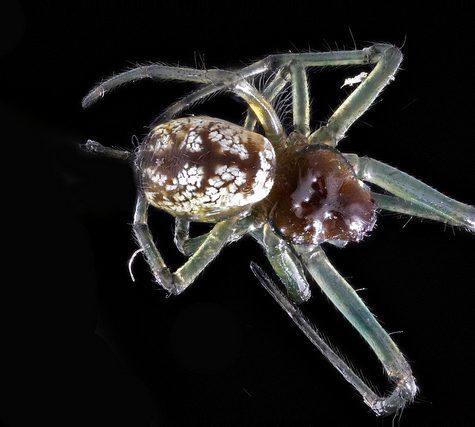

Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs and chelicerae with fangs that inject venom. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all other orders of organisms.[2] Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every habitat with the exceptions of air and sea colonization. As of November 2015, at least 45,700 spider species, and 113 families have been recorded by taxonomists.[1] However, there has been dissension within the scientific community as to how all these families should be classified, as evidenced by the over 20 different classifications that have been proposed since 1900.[3]

Hentzia is a genus of the spider family Salticidae (jumping spiders).
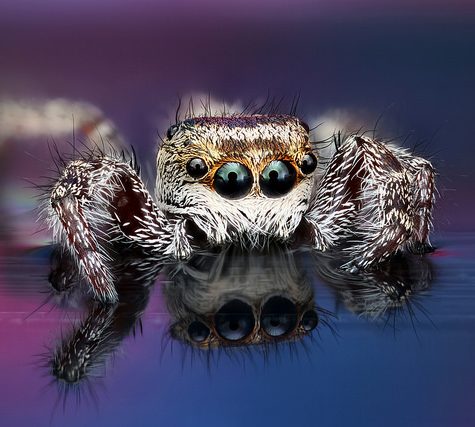

Phidippus princeps is a rare species of jumping spider found in Canada and the United States. These jumping spiders’ vision exceeds by a factor of ten that of dragonflies, which have the best vision among insects.
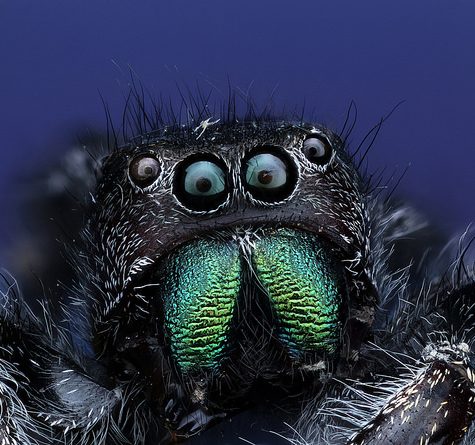

The jumping spider family (Salticidae) contains over 600 described genera and more than 5800 described species,[1] making it the largest family of spiders with about 13% of all species.[2] Jumping spiders have some of the best vision among arthropods and use it in courtship, hunting, and navigation. Although they normally move unobtrusively and fairly slowly, most species are capable of very agile jumps, notably when hunting, but sometimes in response to sudden threats or crossing long gaps. Both their book lungsand tracheal system are well-developed, and they use both systems (bimodal breathing). Jumping spiders are generally recognized by their eye pattern. All jumping spiders have four pairs of eyes, with the anterior median pair being particularly large.

The jumping spider family (Salticidae) contains over 600 described genera and more than 5800 described species,[1] making it the largest family of spiders with about 13% of all species.[2] Jumping spiders have some of the best vision among arthropods and use it in courtship, hunting, and navigation. Although they normally move unobtrusively and fairly slowly, most species are capable of very agile jumps, notably when hunting, but sometimes in response to sudden threats or crossing long gaps. Both their book lungsand tracheal system are well-developed, and they use both systems (bimodal breathing). Jumping spiders are generally recognized by their eye pattern. All jumping spiders have four pairs of eyes, with the anterior median pair being particularly large.

Phidippus princeps is a rare species of jumping spider found in Canada and the United States. These jumping spiders’ vision exceeds by a factor of ten that of dragonflies, which have the best vision among insects.
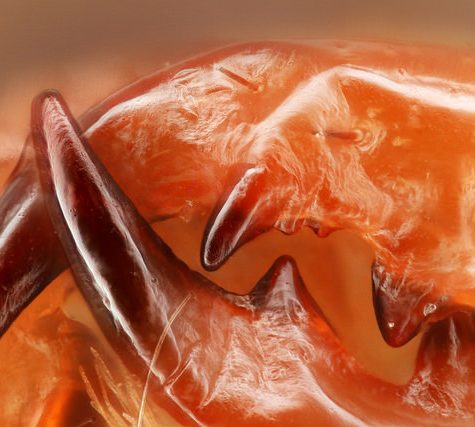
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs[1] and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping pedipalps and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger. Scorpions range in size from 9 mm / 0.3 in. (Typhlochactas mitchelli) to 23 cm / 9 in. (Heterometrus swammerdami).[2]

The jumping spider family (Salticidae) contains over 600 described genera and more than 5800 described species,[1] making it the largest family of spiders with about 13% of all species.[2] Jumping spiders have some of the best vision among arthropods and use it in courtship, hunting, and navigation. Although they normally move unobtrusively and fairly slowly, most species are capable of very agile jumps, notably when hunting, but sometimes in response to sudden threats or crossing long gaps. Both their book lungsand tracheal system are well-developed, and they use both systems (bimodal breathing). Jumping spiders are generally recognized by their eye pattern. All jumping spiders have four pairs of eyes, with the anterior median pair being particularly large.

The jumping spider family (Salticidae) contains over 600 described genera and more than 5800 described species,[1] making it the largest family of spiders with about 13% of all species.[2] Jumping spiders have some of the best vision among arthropods and use it in courtship, hunting, and navigation. Although they normally move unobtrusively and fairly slowly, most species are capable of very agile jumps, notably when hunting, but sometimes in response to sudden threats or crossing long gaps. Both their book lungsand tracheal system are well-developed, and they use both systems (bimodal breathing). Jumping spiders are generally recognized by their eye pattern. All jumping spiders have four pairs of eyes, with the anterior median pair being particularly large.

Ant mimicry or myrmecomorphy is mimicry of ants by other organisms. Ants are abundant all over the world, and potential predators that rely on vision to identify their prey, such as birds and wasps, normally avoid them, because they are either unpalatable or aggressive. Some arthropods mimic ants to escape predation (protective mimicry), while others mimic ants anatomically and behaviourally to hunt ants (aggressive mimicry).[1]
To overcome ants’ powerful defences, mimics may imitate ants chemically (Wasmannian mimicry) with ant-like pheromones, visually (as in Batesian mimicry, though the purpose may also be aggressive mimicry), or by copying microstructure for tactile mimicry.[2]

