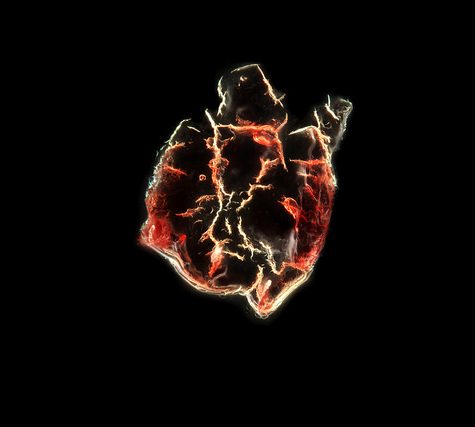
A thrombus, colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulationstep in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to prevent bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when clots obstruct blood flow through healthy blood vessels.
The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system or the vascular system, is an organ system that permits blood to circulate.
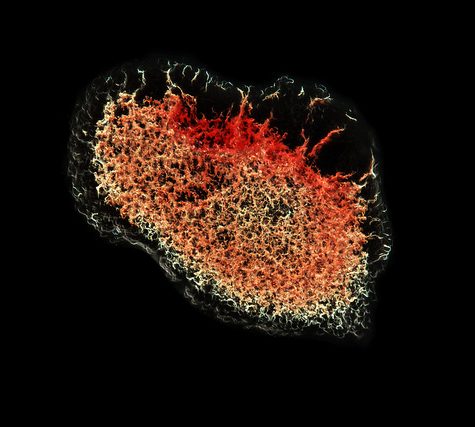
A thrombus, colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulationstep in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to prevent bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when clots obstruct blood flow through healthy blood vessels.
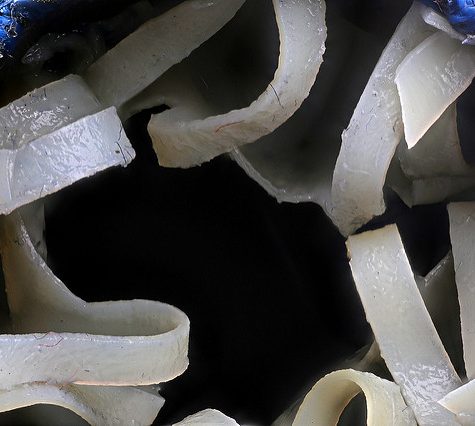
Saliva is a watery substance formed in the mouths of animals, secreted by the salivary glands. Human saliva comprises 99.5% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (which can be used to extract DNA), glycoproteins, enzymes (such as amylase and lipase), antimicrobial agents such as secretory IgA and lysozyme.[1] The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay.[2] Furthermore, saliva serves a lubricative function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the mucosal surfaces of the oral cavity from desiccation.[3]

An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease.[1][2] When one of the four heart valves malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. This requires open-heart surgery.
Valves are integral to the normal physiological functioning of the human heart. Natural heart valves are evolved to forms that perform the functional requirement of inducing unidirectional blood flow through the valve structure from one chamber of the heart to another. Natural heart valves become dysfunctional for a variety of pathological causes. Some pathologies may require complete surgical replacement of the natural heart valve with a heart valve prosthesis.[3]
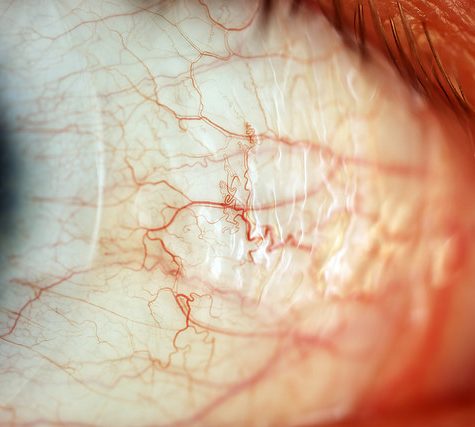
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some elastic fiber.[2] In humans, the whole sclera is white, contrasting with the coloured iris, but in other mammals the visible part of the sclera matches the colour of the iris, so the white part does not normally show. In the development of the embryo, the sclera is derived from the neural crest.[3] In children, it is thinner and shows some of the underlying pigment, appearing slightly blue. In the elderly, fatty deposits on the sclera can make it appear slightly yellow.
The human eye is relatively rare for having an iris that is small enough for its position to be plainly visible against the sclera. This makes it easier for one individual to infer where another individual is looking, and the cooperative eye hypothesis suggests this has evolved as a method of nonverbal communication.
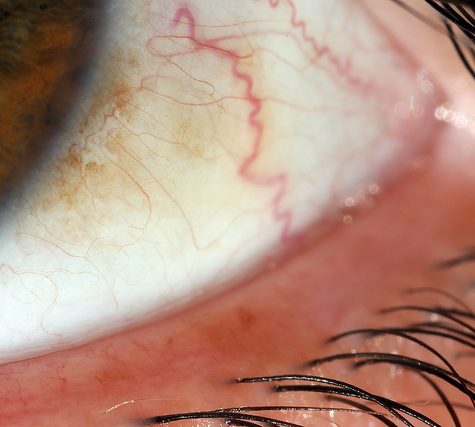
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye, is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some elastic fiber.[2] In humans, the whole sclera is white, contrasting with the coloured iris, but in other mammals the visible part of the sclera matches the colour of the iris, so the white part does not normally show. In the development of the embryo, the sclera is derived from the neural crest.[3] In children, it is thinner and shows some of the underlying pigment, appearing slightly blue. In the elderly, fatty deposits on the sclera can make it appear slightly yellow.
The human eye is relatively rare for having an iris that is small enough for its position to be plainly visible against the sclera. This makes it easier for one individual to infer where another individual is looking, and the cooperative eye hypothesis suggests this has evolved as a method of nonverbal communication.
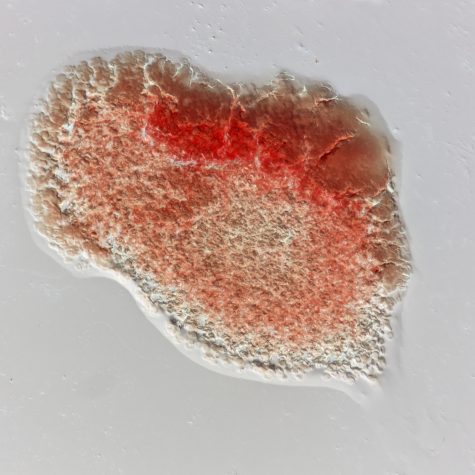
Red blood cells (RBCs), also called erythrocytes, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism’s principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system] RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs or gills and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body’s capillaries. They are between 6-8 microns in diameter.
The cytoplasm of erythrocytes is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiological cell function such as deformability and stability while traversing the circulatory system and specifically the capillary network.
In humans, mature red blood cells are flexible and oval biconcave disks. They lack a cell nucleus and most organelles, in order to accommodate maximum space for hemoglobin. Approximately 2.4 million new erythrocytes are produced per second in human adults. The cells develop in the bone marrow and circulate for about 100–120 days in the body before their components are recycled by macrophages. Each circulation takes about 20 seconds. Approximately a quarter of the cells in the human body are red blood cells.

 Turtledove Diffusers: Godox MF12 Wireless Flash (Set of 2)
Turtledove Diffusers: Godox MF12 Wireless Flash (Set of 2) Fluorescence Kit
Fluorescence Kit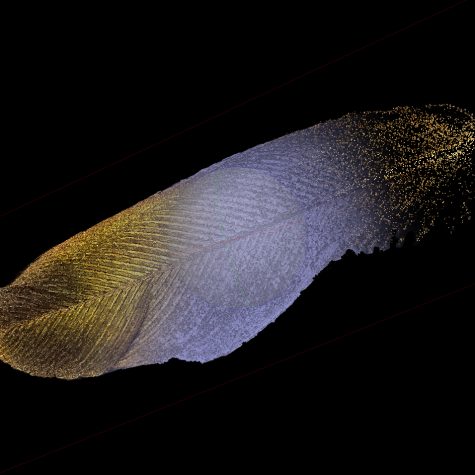 Ruby-throated Hummingbird Tail Feather: 3D Model
Ruby-throated Hummingbird Tail Feather: 3D Model