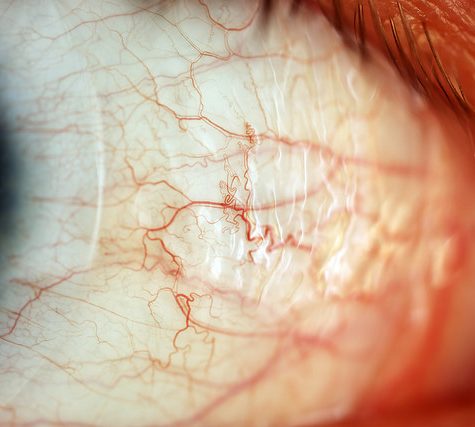
The Nyholm lab studies beneficial host-microbe interactions between the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes, and the bioluminescent bacterium, Vibrio fischeri. Hawaiian bobtail squid are nocturnal predators, remaining buried under the sand during the day and coming out to hunt for shrimp at night neat coral reefs. The squid have a light organ on their underside that houses a colony of glowing bacteria (V. fischeri). The squid uses this bacterial bioluminescence in a form of camouflage called counter-illumination, masking it’s silhouette by matching moonlight and starlight; thus hiding from predators swimming below. The light organ is attached to the ink sac and it can use this ink like a type of shutter to control the amount of light. This likely helps the squid adjust to variable light conditions, for example cloudy nights or a full vs. new moon. In this image of a juvenile squid, you can clearly see the bi-lobed light organ and ink sac in the center of the squid’s mantle cavity.
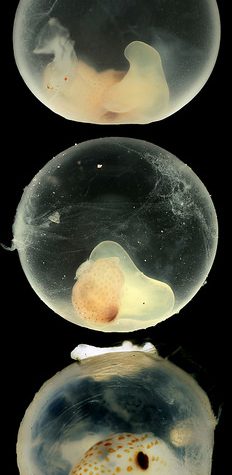
The Hawaiian bobtail squid lay their eggs in clutches on the sea floor, where they take approximately three weeks to develop. This series of macropod images allows us to see the developing squid and monitor embryogenesis. Once the squid hatch, V. fischeri from seawater colonize the light organ within hours. This macropod image allows us to see a close-up view of the ciliated appendage-like structure found on the surface of the juvenile squid’s light organ. Once the squid hatches, the cilia assist in bringing V. fischeri in the seawater to pores at the base of the light organ. These pores lead to inner crypts, where only V. fischeri can enter and colonize. V. fischeri is a relatively rare member of the seawater bacterial community, making up less than 0.1%. The Nyholm lab is trying to understand how the squid’s immune system can differentiate between the symbiont and all the other different kinds of bacteria in seawater.
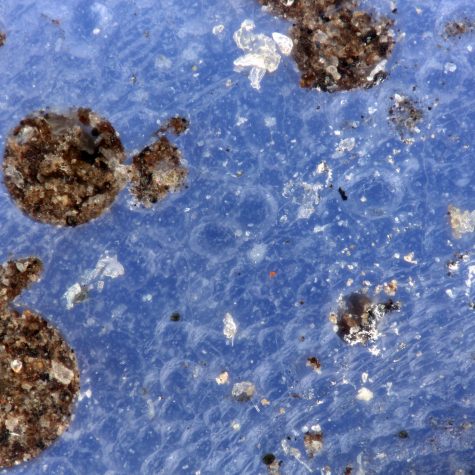
While the light organ of the squid exemplifies a highly specific beneficial relationship between bacteria and host to provide camouflage at night, this organ is only found in some squid species. All squid, however, are capable of another type of camouflage, cryptic coloration. Squid skin contains special pigmented cells called chromatophores that can change the overall color of the squid in seconds. Each chromatophore contains pigment granules surrounded by nerve and muscle fibers. When these muscles are contracted, the pigment sac expands, creating a larger surface area of color. When the muscles relax, the pigment sac can shrink to a small dot, 15 times smaller than their expanded size, hiding the color. In these macropod images you can see relaxed chromatophores on the mantle and contracted chromatophores around the eyes. The macropod images allow us to see these pigment cells in great detail.